The ketogenic diet, commonly called keto, is a low-carbohydrate, high-fat eating plan designed to shift your body into a metabolic state called ketosis. In ketosis, your body burns fat for fuel instead of glucose, which can lead to weight loss and changes in metabolic markers. While many people follow keto for weight management, its effects extend to energy levels, blood sugar control, and appetite regulation.
How the ketogenic diet works
Under typical eating patterns, the body uses glucose, the simple sugar derived from carbohydrates, as its primary fuel. On a ketogenic diet, carbohydrate intake is drastically reduced (often to 20–50 grams per day) and replaced with fats and moderate protein. With limited glucose available, the liver begins producing ketone bodies from fat, small molecules that serve as alternative fuel for the brain and muscles. Transitioning into ketosis usually takes several days of strict carbohydrate restriction. In ketosis, the body becomes more efficient at burning stored fat, which supports weight loss and may improve metabolic flexibility.
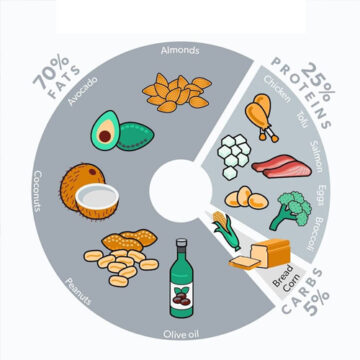
Macronutrient balance on keto
A typical ketogenic macronutrient breakdown emphasizes 70–80% fat, 10–20% protein, and 5–10% carbohydrates. High-quality fats, such as olive oil, avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish, provide energy and support cellular functions. Protein intake is kept moderate to preserve muscle mass without interfering with ketosis, while carbohydrates are restricted to low-glycemic vegetables, berries in small portions, and minimal added sugars. Achieving and sustaining ketosis requires careful attention to macro balance, quality of foods, and consistent monitoring.
Potential benefits and evidence
One of the most well-documented effects of the ketogenic diet is weight loss. Ketosis may suppress appetite hormones and reduce hunger impulses, making it easier for individuals to adhere to lower energy intake. Fat stores are mobilized for energy, and the absence of frequent glucose spikes reduces cravings for sugary foods. Many people report rapid initial weight loss (often due to water loss) followed by sustained fat loss over weeks to months.
Blood sugar and metabolic effects
Reducing carbohydrate intake can have powerful effects on blood sugar and insulin levels. In people with insulin resistance or prediabetes, keto often leads to more stable glucose levels and reduced insulin demand. Some studies suggest improvements in markers like HbA1c, fasting glucose, and triglycerides. However, individual responses vary, and medical supervision is recommended, especially for those with diabetes or metabolic conditions.
Cognitive and energy effects
Some people following keto report improved mental clarity and stable energy throughout the day, potentially due to reduced blood sugar fluctuations. Ketones provide a steady fuel source for the brain, which may reduce “crash and bounce” cycles associated with carbohydrate-rich diets. While research in this area is ongoing, many proponents find the consistency of energy a major lifestyle benefit.
Read also
Mounjaro weight loss explained
Mounjaro represents a new generation of medical weight loss therapy, offering powerful appetite control and metabolic support.
Wegovy: Powerful weight loss solution or overhyped?
Wegovy represents a powerful medical tool for weight management, especially for individuals who have struggled with traditional methods.
Medical weight loss: Medical programs for lasting results
Medical weight loss programs go beyond typical diets and exercise plans. They are supervised by healthcare professionals.
Is Ozempic dangerous? What you need to know
Is Ozempic dangerous? Discover the science behind its benefits, side effects, and risks for diabetes and weight loss.
8 healthy snacks to lose weight
Losing weight doesn’t mean you have to give up snacking. In fact, healthy snacks can help manage hunger, prevent overeating, and support your metabolism.




