Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a common skin condition that causes inflammation, redness, itching, and irritation. Understanding eczema’s causes, triggers, and treatment options is essential for managing flare-ups, reducing discomfort, and maintaining healthy skin.
Understanding eczema and its types
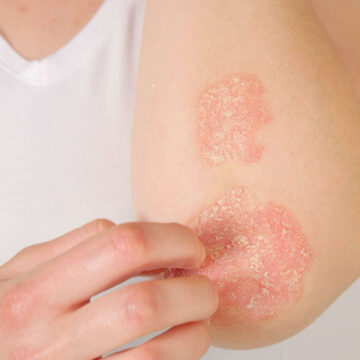
Eczema is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that can appear in several forms. The most common type, atopic dermatitis, often develops on the hands, face, and behind the knees. Other forms include contact dermatitis, nummular eczema, and seborrheic dermatitis. Eczema occurs when the skin barrier is weakened, making it more sensitive to irritants, allergens, and environmental triggers. It often causes dry, scaly patches that can be itchy and uncomfortable.
Who is affected by eczema
Eczema can affect anyone, but it is particularly common in children and people with a family history of allergies, asthma, or hay fever. Adults with eczema may experience recurring flare-ups, often triggered by stress, environmental factors, or skin irritants.
Causes and triggers of eczema
Eczema is often linked to a genetic predisposition and an overactive immune system. When the immune system reacts aggressively to irritants or allergens, it triggers inflammation, redness, and itching.
Environmental triggers
Common triggers include harsh soaps, detergents, certain fabrics, pollution, and changes in weather or humidity. Exposure to these factors can worsen symptoms and prolong flare-ups.
Lifestyle and diet considerations
Some individuals find that certain foods, stress, or inadequate hydration contribute to eczema flare-ups. Maintaining a healthy diet and managing stress levels may help reduce the frequency and severity of symptoms.
Symptoms of eczema
Eczema often manifests as dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. In severe cases, the skin may crack, bleed, or become infected due to frequent scratching. Symptoms vary by age and eczema type, but common signs include redness, thickened skin, rashes, and small bumps that may ooze or crust over. Early recognition allows for timely management and symptom relief.
Eczema flare-ups and patterns
Flare-ups often occur in cycles, with periods of remission and sudden symptom intensification. Triggers such as allergens, harsh weather, or stress can cause the condition to worsen temporarily.
Treatment and management of eczema
Moisturizers and emollients are essential to maintain skin hydration and repair the protective barrier. Topical corticosteroids or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory creams are often prescribed for flare-ups to reduce redness and itching.
Prescription medications and therapies
In moderate to severe cases, dermatologists may recommend oral antihistamines, immunomodulators, or phototherapy. These treatments help manage inflammation and control persistent symptoms.
Natural remedies and lifestyle strategies
Natural remedies such as aloe vera, coconut oil, and colloidal oatmeal can soothe inflamed skin and support healing. Lifestyle adjustments, like using gentle skincare products, avoiding irritants, and maintaining regular hydration, also play a critical role in preventing flare-ups.




